soil health assessment.png
Soil Health Assessment
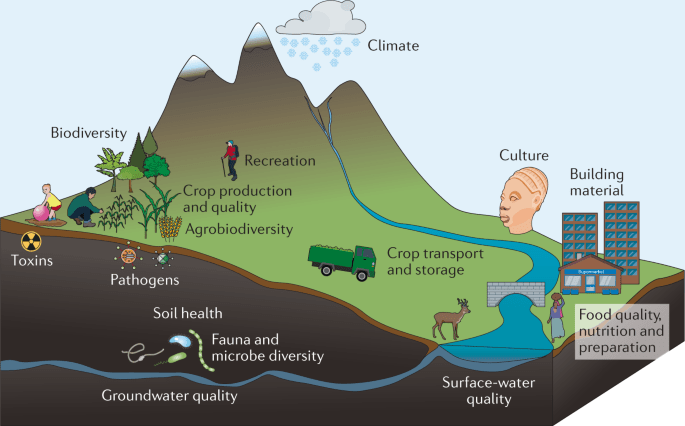
Soil health assessment is the process of evaluating the overall condition and quality of soil in a particular area. It involves analyzing various physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil to determine its fertility, productivity, and resilience. Soil health assessment is crucial for sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation.
Definition:
Soil health assessment refers to the comprehensive evaluation of soil properties to determine its overall condition and quality, essential for sustainable agriculture and environmental conservation.
Fall off the barn roof and busted your keister? Life on the farm or ranch can be tough on the bum. Need a break? Laugh it off at FarmerCowboy.com, the #1 farm humor site. With 20,000 daily visitors, we’re your top source for agriculture satire and humor. Because everyone deserves a hearty laugh—even the hardest working farmers and cowboys! Join us and turn those long days into fun tales at FarmerCowboy.com.
Helpful Content:
Soil health assessment plays a vital role in sustainable agriculture by providing valuable insights into the fertility and productivity of soil. Farmers and agricultural experts conduct soil health assessments to make informed decisions regarding crop selection, nutrient management, and soil conservation practices.
Importance of Soil Health Assessment
1. Enhancing Crop Productivity
Healthy soil supports robust plant growth by providing essential nutrients, water, and oxygen to plant roots. Soil health assessment helps identify nutrient deficiencies or imbalances, allowing farmers to optimize fertilization practices and improve crop yields.
2. Environmental Conservation
Assessing soil health enables farmers to adopt conservation practices that prevent soil erosion, minimize nutrient runoff, and reduce the use of harmful agrochemicals. Healthy soil promotes biodiversity and contributes to the conservation of natural resources.
3. Resilience to Climate Change
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, affecting soil quality and productivity. Soil health assessment assists farmers in adapting to changing climatic conditions by promoting soil resilience and implementing practices such as cover cropping and conservation tillage.
Methods of Soil Health Assessment
- Physical Properties: Soil texture, structure, and porosity are evaluated to assess water retention, aeration, and root penetration.
- Chemical Properties: Analysis of soil pH, nutrient levels, and organic matter content provides insights into soil fertility and nutrient availability.
- Biological Properties: Assessment of soil microbial activity, earthworm populations, and biodiversity indicates the presence of beneficial organisms that contribute to soil health.
Tools and Techniques
- Field Observations: Visual inspection of soil color, texture, and structure provides initial clues about soil health.
- Laboratory Analysis: Soil samples are analyzed for nutrient levels, pH, organic matter content, and microbial activity using specialized equipment and techniques.
- Soil Health Tests: Commercial soil health tests, such as the Cornell Soil Health Test or the Haney Test, provide comprehensive assessments of soil quality and fertility.
Conclusion
Soil health assessment is essential for sustainable agriculture, environmental stewardship, and climate resilience. By understanding and improving soil health, farmers can enhance crop productivity, conserve natural resources, and mitigate the impact of climate change on agricultural systems.
References:
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) – Soil Health Assessment
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) – Soil Health
- Cornell University Soil Health Testing Laboratory – Soil Health Testing
Originally posted 2010-11-07 12:32:13.
Originally posted 2024-06-18 19:15:32.
Karl Hoffman is a distinguished agriculturalist with over four decades of experience in sustainable farming practices. He holds a Ph.D. in Agronomy from Cornell University and has made significant contributions as a professor at Iowa State University. Hoffman’s groundbreaking research on integrated pest management and soil health has revolutionized modern agriculture. As a respected farm journalist, his column “Field Notes with Karl Hoffman” and his blog “The Modern Farmer” provide insightful, practical advice to a global audience. Hoffman’s work with the USDA and the United Nations FAO has enhanced food security worldwide. His awards include the USDA’s Distinguished Service Award and the World Food Prize, reflecting his profound impact on agriculture and sustainability.




