image 6 1.png
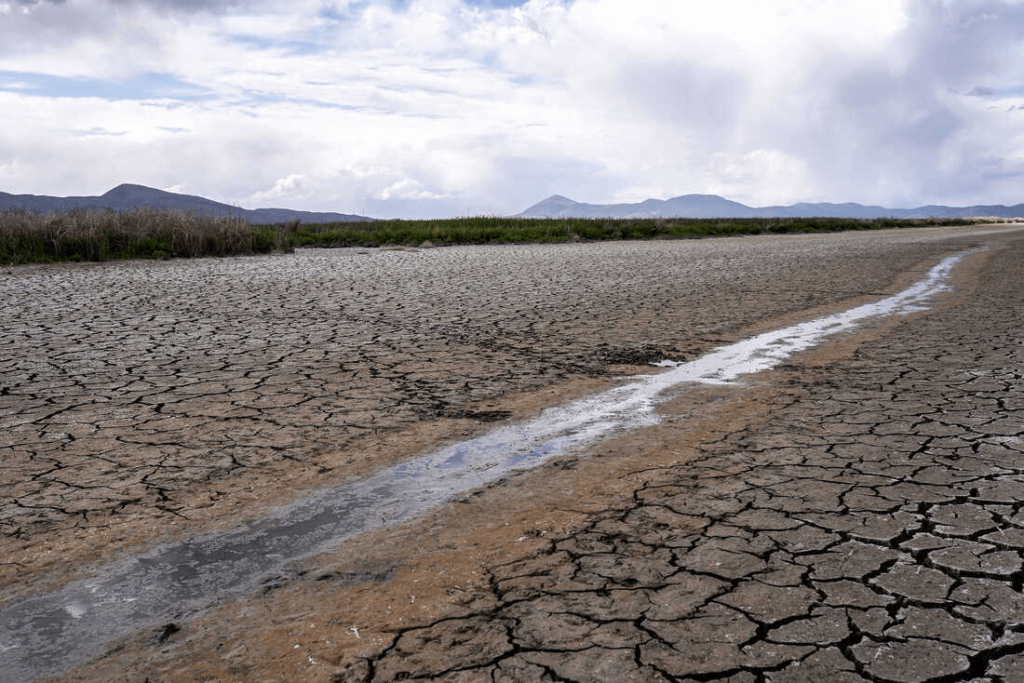
Most natural disasters like tornadoes, earthquakes, or floods occur suddenly and end quickly, however drought follows a slow process and has a longer-lasting impact on people than any other disaster. According to a report published by UNCCD, in 2022, more than 2.3 billion people will face water stress, and around 160 million children may experience severe and prolonged droughts by 2040.
What are the potential causes of drought?
- Climate change 0l
- Changing weather patterns
- Reduction in soil moisture
- Excess water usage
- Deforestation
While the majority are natural causes, water overuse is a man-made cause that can be mitigated and an important factor that needs urgent attention. In this article, we’ll talk about how the drought has affected different nations of Europe and the USA over the years. Then, we’ll discuss drip irrigation and its potential advantages that can help reduce water overuse for agricultural purposes as well as landscape.
How has the drought affected Europe and the US?
A report published by the U.S. Drought Monitor found that over 20 percent of land in the Western States experienced extreme or exceptional drought. Such extreme conditions have a dangerous impact on the agricultural economy, in addition to putting livestock and dairy operations into severe crises. The situation is no different in the European countries, with almost 46% of the continent experiencing “warning” level droughts and 11% to “higher alert” levels. Recently, Italy declared a state emergency in many regions due to its worst drought in 70 years. In addition, France struggled with dried-up drinking water reserves in over a hundred municipalities. Water levels in Europe’s rivers are reaching a critical low point which affects not only the concern of drinking and irrigation water but also affecting the ability to use the waterways for transportation and moving of goods (commercial goods as well as fuels for power plants)
How are nations mitigating excess water usage?
As water levels dipped to dangerously low levels, Italy looked at the worst drought experienced in seven decades. Therefore, a large delegation of Italian companies set forth for Israel to adopt water innovations. Israel reuses 90% of its wastewater for agricultural purposes and is widely regarded as the technology hub for agtech and water technology. For example, Mekorot –Israel’s national water company– has done exceptional research on desalination, purification, and water conservation.
In the US, the year 2022 brought bad news for California as well. The state was facing the driest-ever beginning of the year and staring at unprecedented water restrictions induced by drought. As a result, the Department of Water and Power had to bring in a list of do’s and don’ts for its citizens in the beginning of summer. This plan aimed to reduce water consumption by regulating the water allocation or one-day-a-week limitations on watering activities.
- Assignment of 2 watering days for residents based on an odd-even basis.
- Set time limits for watering plants
- Ban on watering between 9 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Drip irrigation did not fall under any of those restrictions as it is considered a water conserving method of irrigation. This has caused many residential areas to implement new drip irrigation systems replacing sprinklers and other more wasteful formats of irrigation.
How can drip irrigation help control the wastage of water?
Agriculture accounts for 70% of all freshwater withdrawals globally. That’s where drip irrigation can help. As water drips out of holes in pipes buried underneath or closely situated to the ground very close to the plants, it reduces evaporation, and water reaches the stems and roots of crops where it’s needed. Unlike traditional overhead sprinklers, drip water systems use around one-quarter or half of the total amount of water. A report by MIT shows that drip irrigation can help reduce a farm’s total water consumption by almost 60% and improve crop yield by 90%.
Choose drip irrigation technology that suits your needs.
There is no doubt that the benefits of adopting drip irrigation technology are the best way to save water resources. However, the technology is no longer restricted to simple drippers; it has many nuances and aspects that can offer more than just an irrigation technique. There are a variety of dripper solutions on the market today: Round, flat, tape, button, pressure compensating, non drain, compact, non clogging… the list seems endless and each with their own flow rate options.
The bottom line is that choosing the technology that will give you the best possible results can be daunting. With over 35 years of experience under the belt and a combination of innovation engineering and R&D, DRTS specializes in drippers essential for all irrigation sectors including agriculture, mining, and landscaping. With our patented Omniflow technology and a complete range of flat and round drippers that suit every need and solve every challenge, we have become a one-stop solution for manufacturers.
If you’re looking for a trusted partner for effective and innovative drippers, contact DRTS and get your doubts cleared by an industry expert, and select the drip irrigation manufacturing solutions tailored to your market in order to maximize with a personalized touch to improve your ROI. Get in touch with us today!
Source link
2022-09-21 12:05:03
Karl Hoffman is a distinguished agriculturalist with over four decades of experience in sustainable farming practices. He holds a Ph.D. in Agronomy from Cornell University and has made significant contributions as a professor at Iowa State University. Hoffman’s groundbreaking research on integrated pest management and soil health has revolutionized modern agriculture. As a respected farm journalist, his column “Field Notes with Karl Hoffman” and his blog “The Modern Farmer” provide insightful, practical advice to a global audience. Hoffman’s work with the USDA and the United Nations FAO has enhanced food security worldwide. His awards include the USDA’s Distinguished Service Award and the World Food Prize, reflecting his profound impact on agriculture and sustainability.