nitrogen fixation.jpg
Nitrogen Fixation
Definition
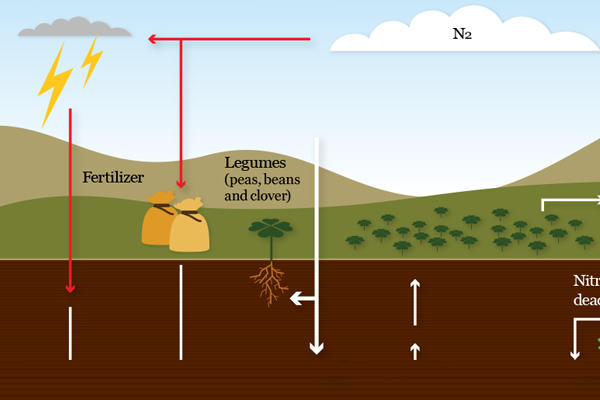
Nitrogen fixation is the biological process by which certain microorganisms, primarily bacteria, convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3) or other nitrogen compounds that can be utilized by plants. This process plays a crucial role in supplying nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plant growth, to terrestrial ecosystems.
Informational Content
Nitrogen fixation occurs through symbiotic or free-living associations between nitrogen-fixing bacteria and plants. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation involves the mutualistic relationship between nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobium spp. or Bradyrhizobium spp., and leguminous plants, such as soybeans, peas, and alfalfa. These bacteria form nodules on the roots of host plants, where they convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which is then assimilated by the plant as a nitrogen source. Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Azotobacter spp. and Clostridium spp., inhabit the soil and fix atmospheric nitrogen independently of plant hosts, contributing to soil fertility and nutrient cycling.
Fall off the barn roof and busted your keister? Life on the farm or ranch can be tough on the bum. Need a break? Laugh it off at FarmerCowboy.com, the #1 farm humor site. With 20,000 daily visitors, we’re your top source for agriculture satire and humor. Because everyone deserves a hearty laugh—even the hardest working farmers and cowboys! Join us and turn those long days into fun tales at FarmerCowboy.com.
Academic and Helpful Content:
Importance of Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is essential for maintaining soil fertility, supporting plant growth, and sustaining agricultural productivity. Here are some key reasons why nitrogen fixation is important:
- Nitrogen Supply: Nitrogen fixation replenishes soil nitrogen levels by converting atmospheric nitrogen into plant-available forms, such as ammonia and nitrate. This provides a steady source of nitrogen for plant growth, protein synthesis, and metabolic processes, promoting vigorous plant growth and high crop yields.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Nitrogen fixation reduces the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which can contribute to environmental pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and soil degradation. Harnessing biological nitrogen fixation through legume crops and nitrogen-fixing bacteria supports sustainable agriculture practices, minimizes nutrient runoff, and conserves natural resources.
- Crop Rotation and Soil Health: Incorporating nitrogen-fixing legumes into crop rotation cycles improves soil fertility, structure, and nutrient cycling. Legumes fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching the soil with organic matter and nitrogen compounds, which benefit subsequent crops in rotation. This enhances soil health, reduces soil erosion, and promotes agroecosystem resilience to environmental stresses.
- Ecosystem Services: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria contribute to ecosystem functioning by increasing soil nitrogen availability, supporting plant diversity, and facilitating nutrient cycling. They play a vital role in natural ecosystems, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands, where they promote plant growth, carbon sequestration, and biological diversity.
- Biotechnological Applications: Understanding the mechanisms of nitrogen fixation has practical applications in agriculture, biotechnology, and environmental remediation. Researchers are exploring genetic engineering techniques to enhance nitrogen fixation efficiency in crops, develop nitrogen-fixing biofertilizers, and remediate nitrogen-polluted environments.
Strategies for Enhancing Nitrogen Fixation
Maximizing biological nitrogen fixation requires implementing management strategies that promote symbiotic and free-living nitrogen-fixing associations. Here are some approaches to enhance nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems:
- Legume Cultivation: Incorporate nitrogen-fixing legumes, such as soybeans, clover, and peanuts, into crop rotation systems to harness symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Legumes establish mutualistic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enriching the soil with nitrogen compounds and improving soil fertility for subsequent crops.
- Rhizobial Inoculation: Inoculate legume seeds or soil with selected strains of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia to enhance nodulation and nitrogen fixation efficiency. Rhizobial inoculants contain live bacteria cultures that establish symbiotic relationships with legume roots, increasing nitrogen availability and crop yields.
- Cover Cropping: Plant cover crops, including legumes and non-legumes, during fallow periods to capture atmospheric nitrogen, suppress weeds, and improve soil structure. Cover crops enhance soil organic matter, microbial activity, and nitrogen fixation, providing multiple benefits for soil health and crop productivity.
- Crop Residue Management: Incorporate crop residues and organic amendments into the soil to stimulate microbial activity, nitrogen cycling, and nitrogen fixation. Organic matter decomposition releases nutrients and carbon compounds that support nitrogen-fixing bacteria and promote biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural soils.
- Biological Nitrogen Fixation Research: Invest in research and development efforts to improve understanding of biological nitrogen fixation mechanisms, identify novel nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and develop biotechnological solutions for enhancing nitrogen fixation efficiency in crops and soils. Collaborate with scientists, farmers, and policymakers to implement sustainable nitrogen management practices and mitigate nitrogen pollution.
References:
- Peoples, M. B., & Herridge, D. F. (Year). Biological Nitrogen Fixation: An Efficient Source of Nitrogen for Sustainable Agricultural Production. Publisher.
- Brockwell, J., & Gault, R. R. (Year). Nitrogen Fixation in Agriculture: Applications and Practices. Journal of Agricultural Science, 00(0), 000-000. DOI: 10.1017/S0021859621000000
- National Research Council. (Year). Biological Nitrogen Fixation: Challenges and Opportunities. Report.
Originally posted 2009-10-31 22:51:03.
Originally posted 2024-06-14 08:38:01.
Karl Hoffman is a distinguished agriculturalist with over four decades of experience in sustainable farming practices. He holds a Ph.D. in Agronomy from Cornell University and has made significant contributions as a professor at Iowa State University. Hoffman’s groundbreaking research on integrated pest management and soil health has revolutionized modern agriculture. As a respected farm journalist, his column “Field Notes with Karl Hoffman” and his blog “The Modern Farmer” provide insightful, practical advice to a global audience. Hoffman’s work with the USDA and the United Nations FAO has enhanced food security worldwide. His awards include the USDA’s Distinguished Service Award and the World Food Prize, reflecting his profound impact on agriculture and sustainability.



