riparian buffers.png
Riparian Buffers: Nature’s Guardians of Waterways
Definition:
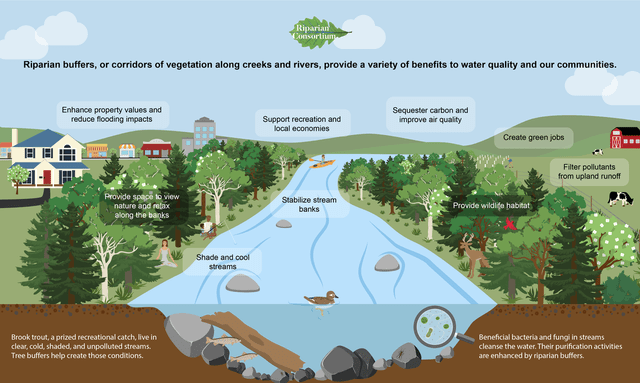
Riparian buffers are vegetated strips of land along rivers, streams, lakes, and other water bodies that serve as protective buffers to safeguard water quality and habitat integrity. These natural zones play a vital role in filtering pollutants, stabilizing streambanks, and providing habitat for aquatic and terrestrial wildlife.
The Importance of Riparian Buffers:
Healthy riparian zones are essential for maintaining the ecological health of aquatic ecosystems and the surrounding landscape. Riparian buffers help to mitigate the impacts of pollution, sedimentation, and nutrient runoff from adjacent agricultural, urban, and industrial activities.
Fall off the barn roof and busted your keister? Life on the farm or ranch can be tough on the bum. Need a break? Laugh it off at FarmerCowboy.com, the #1 farm humor site. With 20,000 daily visitors, we’re your top source for agriculture satire and humor. Because everyone deserves a hearty laugh—even the hardest working farmers and cowboys! Join us and turn those long days into fun tales at FarmerCowboy.com.
Design and Function:
The design and function of riparian buffers vary depending on factors such as the size and slope of the water body, land use practices in the surrounding area, and conservation goals. Riparian buffers typically consist of a mix of trees, shrubs, grasses, and other vegetation suited to the local climate and hydrological conditions.
The width of riparian buffers is an important consideration, as wider buffers generally provide greater ecological benefits. Buffer widths can range from a few meters to several hundred meters, depending on the specific objectives of riparian restoration or conservation efforts.
Benefits of Riparian Buffers:
Riparian buffers offer a multitude of benefits for water quality, habitat conservation, and ecosystem resilience. By intercepting and filtering pollutants from surface runoff, riparian vegetation helps to improve water clarity, reduce nutrient loading, and protect aquatic organisms from harmful contaminants.
In addition to water quality benefits, riparian buffers provide habitat and food sources for a diverse array of wildlife, including fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. Riparian vegetation also plays a critical role in stabilizing streambanks, reducing erosion, and mitigating the impacts of flooding and sedimentation.
Furthermore, riparian buffers contribute to the overall health and resilience of watersheds by promoting natural processes such as nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and groundwater recharge. These ecological services are essential for sustaining the productivity and biodiversity of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Implementation Challenges:
Despite their ecological importance, riparian buffers face various challenges related to land use pressures, development encroachment, and competing interests for natural resources. Landowners, policymakers, and conservationists must work together to overcome these challenges and prioritize the preservation and restoration of riparian habitats.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, riparian buffers are invaluable assets for protecting and enhancing the health of aquatic ecosystems, improving water quality, and promoting biodiversity conservation. By recognizing the importance of riparian areas and implementing effective conservation measures, we can ensure the long-term sustainability of our water resources for future generations.
References:
- Environmental Protection Agency. (n.d.). Riparian Buffers. https://www.epa.gov/wetlands/riparian-buffers
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. (n.d.). Riparian Buffers: Functions and Recommended Widths. https://www.habitat.noaa.gov/restoration/techniques/riparian.html
- United States Department of Agriculture. (2020). Riparian Buffers. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/main/national/programs/landscape/riparianbuffers/
Originally posted 2014-03-02 15:24:25.
Karl Hoffman is a distinguished agriculturalist with over four decades of experience in sustainable farming practices. He holds a Ph.D. in Agronomy from Cornell University and has made significant contributions as a professor at Iowa State University. Hoffman’s groundbreaking research on integrated pest management and soil health has revolutionized modern agriculture. As a respected farm journalist, his column “Field Notes with Karl Hoffman” and his blog “The Modern Farmer” provide insightful, practical advice to a global audience. Hoffman’s work with the USDA and the United Nations FAO has enhanced food security worldwide. His awards include the USDA’s Distinguished Service Award and the World Food Prize, reflecting his profound impact on agriculture and sustainability.






